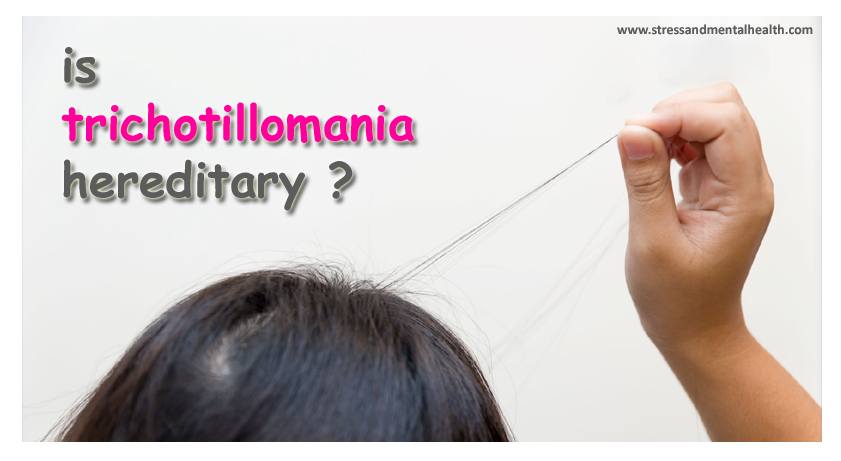
Hello, readers a warm welcome to all of you on the stressandmentalhealth.com website. This post tells you, how to deal with trichotillomania, Is Trichotillomania Hereditary | Hair Pulling Disorder Tied to Genes [2021], Is trichotillomania genetic? Can Vitamin D deficiency cause trichotillomania?, Cause, Trichotillomania Research, Does hair grow back after Trichotillomania, Does trichotillomania go away? Is it possible to stop Trichotillomania, Trichotillomania foods to avoid?
Introduction
“Yes, Is Trichotillomania Hereditary, but other factors are also responsible for the condition. Stress, anxiety, chemical imbalance in the brain, change in hormonal level during teenage years also triggers it.”
Is Trichotillomania Hereditary
Is Trichotillomania Hereditary, First of all, we may discuss whether Trichotillomania is hereditary or genetic? Yes, it can be, but other factors also play an equal role in it.
All people are not born with this disease. In some cases, it develops in childhood and adolescence, which is due to some sort of trigger of anxiety and stress. It is due to distress in personal life.
In some cases, a combination of environmental and biological factors tends to influence the presence of mental health disorders, including Trichotillomania. By identifying it as a genetic disease or an environmental disorder, people can prevent and treat the condition.
Is Trichotillomania Genetic?
In many studies, it is clearly proof that trichotillomania is a genetic and inherited mental health condition. It is believed mutation of SLITRKI genes only accounts for about 5 % of all the existing cases of trichotillomania and additional environmental and biological factors are also plays an important role in the emergence of trichotillomania.
People who are suffering from a high level of stress and tension are more prone to hair-pulling disorder due to uncomfortable feelings. Brain scans show small differences in some areas of the brain of people suffering from trichotillomania compared to people not suffering from trichotillomania. It shows that abnormalities in the brain also plays important role in the condition development.
Can Vitamin D deficiency cause trichotillomania?
Vitamin D deficiency has been correlated with nonscarring alopecia including alopecia areata or female pattern hair loss. It was theorized that hair loss secondary to vitamin D deficiency in patients susceptible to trichotillomania may exacerbate this obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Cause
The cause of Trichotillomania is a chemical imbalance in the brain, just like obsessive-compulsive disorder(OCD) change in hormone levels during puberty.
Trichotillomania Research
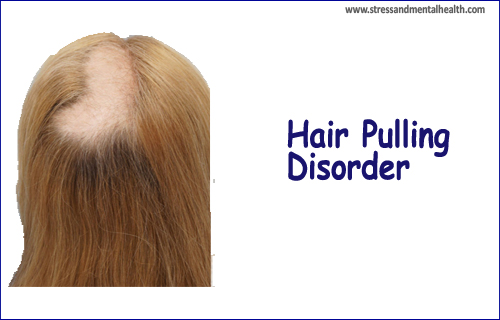
On the basis of the findings of the study, one can conclude there is clear proof showing Trichotillomania is an inherited mental health condition. People with high levels of stress and tension are more prone to hair-pulling disorder as a way to cope with uncomfortable feelings. Brain scan shows that people with Trichotillomania have small differences in some areas of the brain compared to people without the disorder, which suggests that brain development abnormalities could play a role in the condition development.
So, it is clear that this disease is inherited but other factors play an equal role.
Does hair grow back after Trichotillomania
In most cases, hair will grow back. Though it will take a long time about 2 to 4 years you will see your hair return.
How to stop hair pulling: (Is Trichotillomania Hereditary)
Occupy or busy yourself with something else. A person suffering from milder Trichotillomania may be able to stop pulling hair by replacing this repetitive action with something else.
Does trichotillomania go away?
Trichotillomania mostly develops just before or during early teens mostly in the ages of 10 to 16 years and it remains continued life long. Infants also can be prone to hair pulling but it might be mild and goes away on its own without any treatment. However, below mentioned activities may also help you to get rid of this disorder.
- Squeeze a stress ball.
- Form a ball with your fist and tighten the muscles in that arm.
- Use a fidget toy.
- Wear a tight-fitting hat on your head.
Is it possible to stop Trichotillomania
There is no cure but it can be managed. Psychotherapy by a specialist would be the ideal method to deal with it.
Is Trichotillomania Hereditary? Are you born with a hair-pulling disorder
In most cases, no child is born with this disorder. It may occur in teenagers due to various reasons which insist children pluck the hair of different parts of the body such as head, eyebrows, eyelashes, face, arms ears, nose, etc.
Some more common areas such
as underarms.
beards.
chest.
The reason may be tension, anxiety, anger, loneliness, etc.
The Patient feels tension due to the overburden of study in school and goes under depression, starts pulling hair.
The patient feels anxiety due to negligence at home, school. Which compelled them to start pulling the hair of different parts of his body.
The patient feels anger due to dissension in the family or with friends, he started pulling hair.
The reason might be someone, consequences are very dreadful. After the pulling of hair from different parts of the body dreadful spots appear on the affected area of the body, from where hairs are pulled.
People suffering from this disease often pull only one or two hairs at a time but these hair-pulling episodes last for hours at a time. It goes into remission–like a state where the patient may not feel the urge to pull for days, weeks, months, or in any case years.
In many cases, it exhibits hairs of different lengths, broken hairs with dull ends, new growth with tapered ends, some broken mid-shaft, or some uneven stubble. Overall hair density is normal. Hair often pulled out leaving an unusual shape. An individual suffering from Trichollmania may be secretive or shameful of the hair-pulling behavior.
Some people suffering from this disease wear hats, wigs, false eyelashes, eyebrow pencils, or style their hair in an effort to avoid attention. On the other hand low-stress environments, some exhibit no symptoms whatsoever. This hair pulling often resumes after leaving this environment In some cases, people with Trichollmania may feel they are the only person with this problem due to delay in reporting.
Nowadays research is being carried out by scientists in various countries. Scientists have discovered and observed that PRP therapy has a vast role in the growth of hair. It is possible in the matter where the patient stops the hair-pulling. However further research is also being carried out in this field by scientists of various countries.
Trichotillomania foods to avoid?
Trichotillomania is also caused due to food allergy, especially it is linked to Gluten. In the case where the gut is not functioning properly, the brain itself will not work properly due to malabsorption. So we must avoid the intake 0f gluten food.
Intake of more sugar also leads to an imbalance of neurotransmitter, and increase the urge to pull hair. Intake of too much sugar also increased the release and destruction of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are rich in mood-stabilizing properties, and deficiency thereof is linked to mood disorders such as depression.
Therefore excess sugar intake caused depressed mood and aggravates underlying causes of hair-pulling urges.
Thus we must avoid such foods.
Frequently Asked Question About Is trichotillomania hereditary
Q. Is hair pulling hereditary?
Ans. Hair pulling, a psychiatric disease that compels people to pull their hair is genetic. It runs from family to family.
Q. Does trichotillomania ever go away?
Ans. Trichotillomania does not go away on its own. It is a mental health disorder that requires medical treatment.
Q. What is the best medicine for hair pulling?
Ans. There is no specific medicine for the treatment of this disorder. However, some anti-depressant medicines may help to control the symptoms. The patient may contact a psychiatrist for treatment.
Q. Is hair pulling is a form of OCD?
Ans. It is an obsessive-compulsive related disorder.
Q. Is hair pulling is a mental disorder?
Ans. It is a mental disorder that involved a recurrent, irresistible urge to pull out hair from the scalp, eyebrow, and other parts of the body, in spite of trying to stop.