The function of stomach in digestive system, The human body is a miracle gifted by god. Every part of our body has its own importance. Our body is incomplete in the absence of anyone part. So the human digestive system is also very important and plays an important role in the development of an immune system, proper digestion of food, maintenance of every part of our body. As soon as we eat food in our mouth.
Our teeth began to grind the same, salivary glands spread saliva, tongue help mix saliva in-ground food. The gastric gland in our stomach and various chemical changes occur in our duodenum, small intestine, and large intestine. Our pancreas, liver, and gall bladder also play a vital role in the digestive system.
The entire alimentary canal is lined by a mucus membrane. From lips to the end of the esophagus this is the stratified epithelium. And from the stomach to the anal canal this lining is composed of the columnar cell, and the anal canal is also lined with stratified epithelium. So in this way, our whole alimentary tract has been made safe by these linings.
So describe as under
Structure and function of the human digestive organ
Glands provide digestive juices include salivary glands, gastric glands in the stomach, bile in the liver, pancreatic juice in the pancreas. All these organs and glands help to the physical and chemical breaking and changes of food consumed and elimination of indigestible food.
So I am discussing here the importance of the stomach of our body in the digestive process.
Also read – large intestine function in digestive system
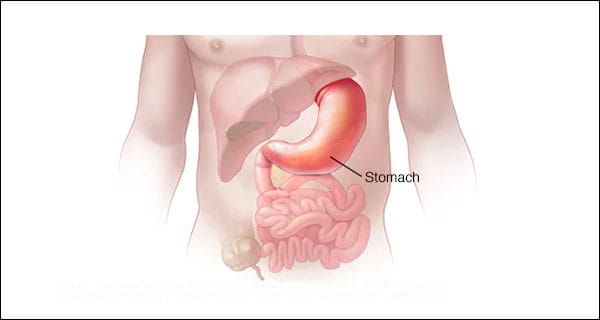
Stomach
the function of stomach in digestive system, The stomach is the most dilatable part of the human body. It communicates with the esophagus by cardiac orifice and with the duodenum by the pyloric orifice.
The stomach is subdivided into four regions
- The fundus is an expended area curving up above the cardiac opening
- The body or intermediate region
- The central and largest portion region
- The antrum, the lowermost region, a funnel-shaped portion of the stomach, and the pylorus, narrow portion joining point of the stomach and small intestine
The entry point and exit point of the stomach contain cardiac and pyloric sphincter muscle, that keeps the neighboring region closed except when the food is passing through there.
The stomach consist of four coats; An outer on the peritoneal coat, a serous covering. Three-layer of muscular coat, such as longitudinal fibers, circular fibers, and oblique fibers. A submucous coat of aerosol tissue contains the blood vessels and lymphatic’s. A mucous coat is thick and soft and is arranged in corrugated folds, rugae, it disappears when the stomach is distended by food.
The stomach can expand its size according to the amount of food received by it. When contracted, the numerous fold disappears as soon as the wall is distended. The thick mucus membrane lining of the walls is densely packed with small gastric glands these glands secrete a mixture of enzymes and hydrochloric acid, which partly digest protein and fats.
The stomach muscle is hardly ever inactive. As food enters the stomach, they relax briefly, then begin to contract. Periodic contractions churan and knead food into a semifluid mixture called chyme Peristaltic contractions persist after the stomach empties and increasing with time, may become painful. Such hunger pangs may also be related to the amount of sugar in the blood. When the level of sugar is decreased, hunger can be felt without the intervention of the stomach.
The stomach does not absorb food and water. But it absorbs iron and highly fat-soluble substances such as alcohol and some drugs directly. The function like secretions and movements of the stomach is controlled by the vagus nerve and the sympathetic nervous system, emotional stress can alter the normal function of the stomach.
Also read – pharynx function in digestive system
Also read – mouth function in digestive system
Also read – 9 best teas for digestion you should know
What is the disease of the stomach?
A common disease of the stomach is peptic ulcer, gastritis, and cancer.
There is a tiny duct of the gastric gland, and the surface, where the duct opens, is lined with columnar epithelium continuous with that of the mucous surface of the stomach. There is a cardiac gland lying at the esophageal opening. These are tubular glands, secrete an alkaline mucus.
There are predominate glands of our body, called tubular glands which contain different types of cells. Some cell produces pepsin, some produce gastric acid, others produce mucin. The pyloric glands produce alkaline mucus. The stomach receives blood from the gastric and splenic arteries. The nerve supply is derived from the vagus and coeliac plexus of the sympathetic system.
Function of stomach
In common language, the stomach works as a grinder and mixer in our digestive system. The function of the stomach is to do muscular contraction and mix the food with gastric juice. The stomach does not pass whole food at one time. It passes about half an ounce at a time through a pyloric opening into the duodenum. The contents received from the stomach are high in acid, whereas the content in the duodenum is less acid.
So the small quantity of content received from the stomach neutralizes in the duodenum by alkaline juice of duodenum, pancreas, and bile. And the neutralization of the present content, the duodenum receives another half ounce of content from the stomach. This function remains continued till the stomach is empty.
The glands in the mucous coat of the stomach secrete a digestive fluid, named gastric juice.
That is colorless acid fluid, which contains 0.4% hydrochloric acid, which acidifies all the food we intake, and kills all the germs, and makes the food harmless. The gastric juice contains Pepsin, Rennin, gastric lipase.
The stimulation of gastric juice is partly nervous and partly chemical. Secretion starts as soon as we eat food. Further taste of secretes nervous secretion. In nutshell, the stomach receives the food and work as a reservoir for a short time, mix hydrochloric acid in a paste of food received, convert protein into peptone, change milk into curd and casein set free, digestion of fat started, formed anti-anemic factor, chyme, liquefied stomach content passed into duodenum.
Frequently Asked Question About Function of stomach in digestive system
Q. What is the function of the stomach in digestion?
Ans. The stomach is a hollow organ, that holds food during the period when it is mixed with stomach enzymes. These enzymes break down the food into a usable form. Cells present in the lining of the stomach, secrete a strong acid and enzymes that carry out the process of breakdown of food.
Q. How does the stomach work?
Ans. There are many glands and cells in our stomach that secrete acid and enzymes. These acids and enzymes play an important role in the digestion of food. Ridges of muscle tissue called rugae line the stomach. Muscle’s of stomach contract periodically, churning food to enhance digestion. The pyloric sphincter is a muscular valve that opens to allow food to pass from the stomach to the small intestine.